Both drive-in and drive-thru racking are high-density storage racking systems with few aisles that can make the most use of storage space. Are you familiar with drive-in and drive-thru racking? Which type of racking better fits your warehouse storage space? This article gives detailed instructions of drive-in drive -thru racking, and help you make decision on choosing your storage system.
What is drive in racking system and how does it work?
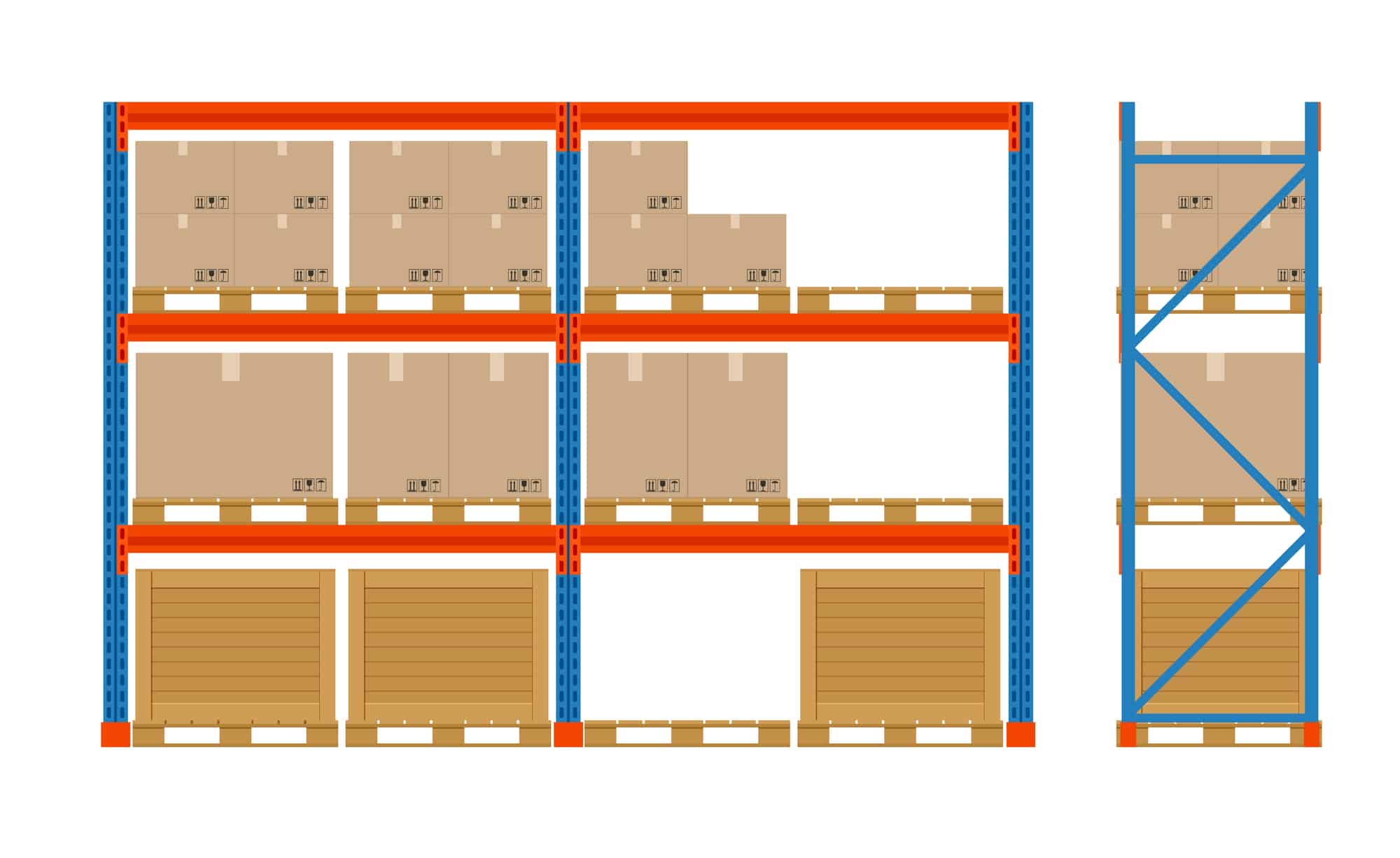
Drive in racking is a first in last out (FILO) storage racking system usually made up of upright frames, beams, pallet support rails, ground rails, and top and back bracings, and with single entrances into the rack system. Drive-in racking is composed of multiple connected aisles, in which pallets are stored on support rails. The forklift driver puts the first pallet into the deepest pallet position of lane. Then he drives out, pick up another pallet, and drives into to put the second pallet in front of the first pallet. Cycle like this until the lane is full. The pallet placed first is in the deepest position of the racking, and the later placed pallet is much closer to the racking entrance. When unloading pallets in the storage lane, the pallet at the lane entrance should be unloaded at first, then slowly drive the forklift into the storage lane following the designated path and unload pallets one by one with cautious.

Components of Drive-in Racking
Upright Frame – The upright frame is the most important part of the drive-in racking system. It provides the major support to the whole system. It is consisted of uprights columns and bracings.
Top Beam – The beams on the top part of the drive-in racking system are called top beams. They offer balance on the top of each bay.
Top Bracing – Top bracings are connected with top beams to connect the system on top of each bay. The parts are connected by buckles or nuts.
Double Support Arm – Double-side arms are the gadgets that hold pallet rails. They are anchored on the upright posts.
Single Support Arm – Single-side arms, just like double-sided arms, are also used to provide support for the pallet rails. The only difference is that the needs of single-sided arms are much less than double-sided arms, since only the start bay and end bay require single-sided arms.
Pallet Support Rail – The rails are where you lay your pallets on. You lay your pallets between two rails, where the pallets can be pushed into the deepest position of the system to leave empty space for new coming pallets.
Post Protector – Usually colored in yellow, most post protectors are in bold color for forklift to avoid the vulnerable part of the racking system. Post protectors are designed to protect the uprights for racking safety.
Floor Guide Rail – Floor guide rail is designed to guide the forklift drivers to move safely in the racking system. It can quickly stop forklift wheels before hitting the racking system.
What are the advantages of drive-in racking system?
High-density storage
Drive-in racking maximizes the use of available space by eliminating the need for aisles between the racking rows. The system allows forklifts to drive directly into the storage lanes, creating a dense block of storage. This high-density configuration enables efficient utilization of space, making it ideal for storing large quantities of homogeneous products.
Increased storage capacity
By eliminating aisles, drive-in racking can significantly increase the storage capacity compared to traditional selective racking systems. It reduces the wasted space typically occupied by aisles, allowing for more pallet positions within the same footprint. This is particularly advantageous in warehouses with limited space or when maximizing storage capacity is a priority.
Cost-effective
Due to its high-density storage capability, drive-in racking can help reduce construction and operational costs. It requires fewer aisles and provides more storage positions within the available space, which means you can store more products without the need for additional square footage. This can result in cost savings in terms of land, construction, and ongoing operational expenses.
Efficient stock rotation
Drive-in racking follows the Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) principle. This makes it suitable for products that do not require strict rotation or have a long shelf life, such as products with no expiration dates or where inventory turnover is not critical. It allows for easy access to the latest loaded items, making it convenient for applications where the order of loading and unloading is not critical.
Simplified inventory management
With drive-in racking, it is easier to manage inventory as large quantities of the same product are stored together. This simplifies stock tracking and improves visibility, making it convenient for inventory control and accurate stock management.
Where to use drive-in racking?
Drive-in racking is commonly used in industries that deal with large quantities of homogeneous products and where high-density storage is a priority.
Some of the industries where drive-in racking is often employed include:
Food and Beverage
Drive-in racking is widely used in the food and beverage industry, especially for storing perishable goods such as dairy products, fruits, vegetables, and frozen foods. It allows for efficient storage of bulk quantities while maintaining product integrity and facilitating stock rotation as needed.
Cold Storage and Freezers
Drive-in racking is particularly suited for cold storage and freezer environments where temperature-controlled storage is required. The high-density configuration optimizes space utilization and facilitates the storage of temperature-sensitive products, such as frozen foods, pharmaceuticals, or vaccines.
Manufacturing
Drive-in racking is utilized in manufacturing facilities to store raw materials, work-in-progress inventory, or finished goods. It is suitable for industries with high-volume production and limited SKU diversity, such as automotive, electronics, or consumer goods manufacturing.
Wholesale and Distribution
Wholesale and distribution centers that handle large quantities of products can benefit from drive-in racking. It enables efficient storage and retrieval of goods, streamlining the order fulfillment process and maximizing storage capacity for products with low SKU variation.
Retail and E-commerce
Drive-in racking can be found in retail and e-commerce warehouses that deal with fast-moving consumer goods or products with consistent demand. It allows for efficient storage of products that are frequently restocked, facilitating streamlined inventory management and order picking processes.
Pharmaceutical and Healthcare
Drive-in racking is suitable for the pharmaceutical and healthcare industries where large quantities of products, such as medicines, medical supplies, or hospital equipment, need to be stored efficiently. It provides a compact and organized storage solution while maintaining product integrity and accessibility.
Regular Maintenance of Drive-in Racking System
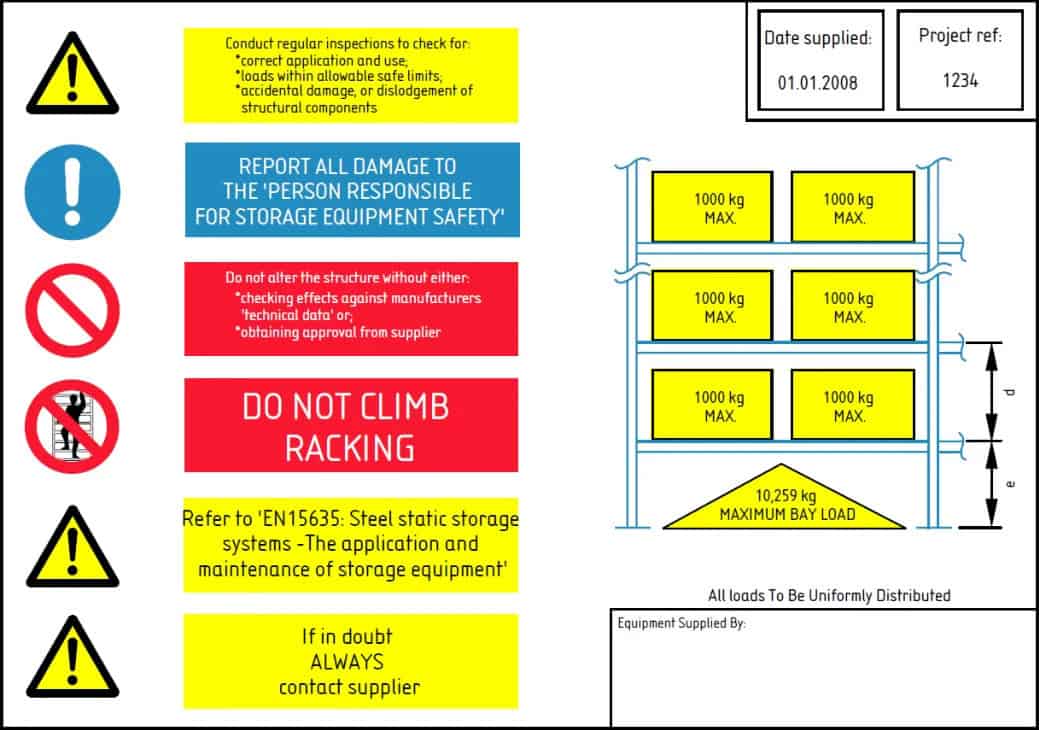
- The size of the pallets you use should match the dimension of the drive-in racking system. Generally, the racking supplier would mark the dimensions clearly on their products.
- Regular check to make sure all parts of the system are working properly on a regular basis. Report the damage related to any part of the system, like bend beams or uprights. Then an immediate replace or repair should be arranged.
- Check safety locks on beams – any damaged or broken locks should be replaced immediately.
- To avoid the metal getting rusted, check the powder coating of the metal parts regularly.
- Regular check for pallets condition. Replace those with signs like cracks, breaks or severe damage.
- Make sure that all bolts, nuts, and other little hardware are all well tightened.
- Regularly train warehouse personnel for the correct use of forklifts and loading and unloading techniques. Improve their awareness and sense of responsibility for maintaining a safe environment in the warehouse.
Drive in Racking System vs Selective Pallet Racking System
Drive-in racking system and selective pallet racking system are two different storage systems that offer distinct advantages and are suitable for different warehouse applications. Let’s compare the two from the following five points.
Storage Density:
Drive-in racking: Drive-in racking provides high-density storage by eliminating the need for aisles between racking rows. It allows forklifts to drive directly into the storage lanes and stack pallets one behind the other, maximizing space utilization.
Selective pallet racking: Selective pallet racking offers lower storage density compared to drive-in racking. It requires individual aisles for each row of racking, reducing the overall storage capacity.
Accessibility
Drive-in racking: Drive-in racking follows the Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) principle, where the last pallet loaded is the first one that can be accessed for retrieval. This makes it suitable for applications where strict stock rotation is not critical.
Selective pallet racking: Selective pallet racking follows the First-In, First-Out (FIFO) principle, enabling easy access to any pallet within the racking system. This is beneficial for applications where stock rotation and quick access to specific SKUs are important.
Product Variety
Drive-in racking: Drive-in racking is ideal for storing large quantities of homogeneous products. It is suitable for applications where there is limited SKU diversity or where bulk storage is needed.
Selective pallet racking: Selective pallet racking accommodates a wide variety of product sizes, shapes, and SKUs. It allows for individual pallet access, making it suitable for warehouses with diverse product ranges and frequent inventory turnover.
Order Picking
Drive-in racking: Drive-in racking is not designed for individual pallet access, which can make order picking more time-consuming and less efficient compared to selective pallet racking.
Selective pallet racking: Selective pallet racking offers excellent accessibility to each pallet, making it well-suited for order picking operations and rapid inventory turnover.
Cost
Drive-in racking: Drive-in racking generally requires a lower initial investment compared to selective pallet racking because it utilizes less aisle space and has a simpler structural design.
Selective pallet racking: Selective pallet racking may involve higher initial costs due to the need for more aisles and potentially more structural components.
Overall, the choice between drive-in racking system and selective pallet racking system depends on factors such as storage density requirements, stock rotation needs, product diversity, order picking efficiency, and budget considerations. Some warehouses may even combine both systems to accommodate different storage needs within their operations.
Comparison Between Drive-in Racking and Push Back Racking
Push back racking is also a type of high-density pallet storage system with LIFO principle, meaning that the last pallet loaded onto a lane is the first to be unloaded. Both drive-in and push back are last-in first-out storage systems. But the two systems have some difference on operating method and selectivity.
| Drive-in Racking | Push Back Racking | |
| Storage and Retrieval Method | Drive-in racking also operates on a Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) principle. Pallets are stored on rails or beams, and forklifts drive directly into the rack structure to deposit or retrieve pallets. The last pallet loaded is the first to be unloaded. | Push Back Racking: Push back racking operates on a Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) principle. Pallets are loaded onto inclined rails, and when a new pallet is added, it pushes the previously loaded pallet(s) further back into the lane. When unloading, the front pallet is removed, causing the remaining pallets to roll forward for retrieval. |
| Access and Selectivity | Drive-in racking offers limited selectivity. It is designed for storing large quantities of the same product or SKU, as the forklift must enter deep into the rack structure to access or retrieve pallets. | Push back racking provides greater selectivity compared to drive-in racking. Each level of push back racking can hold a different SKU, allowing for easier access to specific pallets. |
| Handling and Operation | Drive-in racking allows forklifts to drive directly into the rack structure, making it suitable for manual or semi-automated operations. It requires careful forklift operation to avoid damage to the racks or pallets. | Push back racking requires the use of carts or trays on inclined rails, which can automatically move pallets within the rack structure. It typically involves a higher degree of automation and requires specialized equipment for loading and unloading. |
What is drive through racking?
Drive-through racking, also known as drive-thru racking, is a type of storage system similar to drive-in racking but with an additional access point. It is designed to allow forklifts to enter the storage lanes from both ends, providing a drive-through capability. This enables greater flexibility in terms of pallet access and stock rotation compared to drive-in racking.
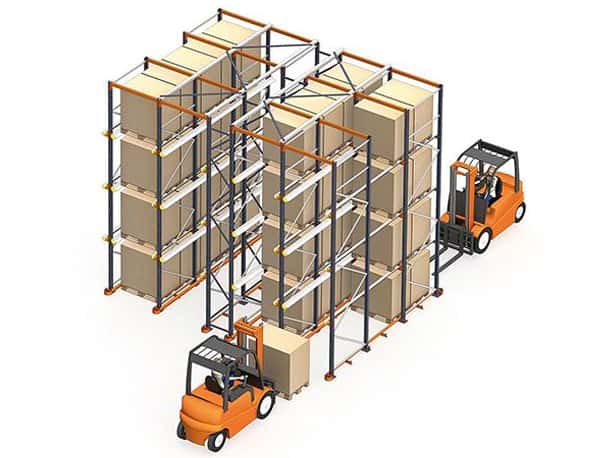

What is the difference between drive in and drive through racking?
Drive-thru racking is a system that allows forklifts or pallet jacks to enter the racking structure from both sides. This means the racking structure has two access points, usually with one entry point and one exit point. Pallets can be loaded from one side and retrieved from the other, creating a first-in, first-out (FIFO) flow. While drive-in racking has only one access for pallets loaded and retrieved. Drive-in racking is first-in, last-out (FILO).
Simply speaking, drive-thru racking is FIFO (first-in, first-out), and drive-in racking is FILO (first-in, last-out).
When to choose drive through racking?
Drive-through racking is typically chosen when
FIFO Inventory Rotation
If your inventory requires strict adherence to a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory rotation system, drive-through racking is the preferred choice. This is because the dual-entry design allows for easy access to the oldest pallets, ensuring proper inventory rotation and minimizing the risk of product obsolescence or expiration.
High Selectivity
Drive-through racking offers higher selectivity compared to drive-in racking. If you need frequent access to different pallets or SKUs, or if your inventory consists of various products with different turnover rates, drive-through racking allows for easier and quicker access to specific pallets. This is especially advantageous in industries with fast-moving or time-sensitive goods.
Inventory with Expiration Dates
Drive-through racking is suitable for products that have expiration dates, such as perishable goods or items with limited shelf life. By following a FIFO system, you can ensure that the oldest products are accessed and used first, reducing the risk of spoilage or waste.
Things to consider when designing drive-thru racking system
When designing a drive-through racking system, several factors should be taken into consideration to ensure an efficient and safe storage solution.
Inventory Characteristics
Understand the characteristics of the inventory you will be storing, including the size, weight, and dimensions of the pallets or goods. This information is crucial for determining the appropriate rack configurations, such as the height, depth, and spacing between racks.
Inventory Turnover and Accessibility
Analyze the turnover rate of your inventory and consider the frequency of access required. If you have fast-moving products or need quick and frequent access to specific pallets, you may need to optimize the layout to ensure efficient retrieval.
Space Utilization
Assess the available space in your facility and determine the optimal layout for the drive-through racking system. Consider the dimensions of the racks, aisle widths, and the number of aisles required to accommodate your inventory volume. Balancing storage density with the ability to maneuver forklifts safely is essential.
Forklift and Equipment Requirements
Take into account the type and capabilities of the forklifts or material handling equipment that will be used in the system. Consider factors such as the maximum lift height, turning radius, and load capacity of the equipment to ensure the design allows for safe and efficient maneuvering within the aisles.
Safety Considerations
Prioritize safety when designing the system. Ensure that the racking structure is designed to withstand the weight and loads it will bear and comply with relevant safety standards and regulations. Include appropriate safety features such as rack protection, floor markings, and clear signage to enhance visibility and prevent accidents.
Entry and Exit Points
Determine the location and number of entry and exit points based on your operational needs and traffic flow. Consider the layout of your facility and the flow of goods to optimize the movement of forklifts and minimize congestion.
In general, both drive-in and drive-thru racking are high-density storage racking systems with few aisles that can make the most use of storage space. If you still hesitate on drive-in or drive-thru, please CONTACT iWarehousing team and we’d love to help.